The structure and chemistry of hair provide the basis for good hair care and styling. Hair is mostly keratin protein. Keratin is high in sulfur amino acids, especially cysteine. Cysteine bonds give hair strength, stretch, and texture. Hair’s pH level matters too. It refers to its acidity or alkalinity. An acidic pH, below 7, closes the hair cuticle. This makes hair smoother and color brighter. An alkaline pH, above 7, opens the cuticle. This allows the color to penetrate deeper. On the other hand, too much alkalinity causes dryness and breakage. Chemical processes, like perming and relaxing, change the disulfide bonds. They reshape or straighten hair. They are later reconstituted to set the new shape. A good grasp of pH and disulfide bonds will let the hairdresser safely achieve different styles and colors.
Understanding Dye Types and Chemistry
Hair dye chemistry involves several types of dyes. Each has different effects on hair. So-called oxidation dyes are most commonly used for permanent color. These depend on a chemical reaction started by an oxidizing agent, like hydrogen peroxide. This converts colorless precursor dyes into colored molecules. These can penetrate the hair shaft and bind to keratin. They achieve long-lasting color and reliable gray coverage. In contrast, semi-permanent and temporary colors use direct dyes. Their larger pigment molecules coat the hair without entering it. Therefore, they are not harmful but not permanent either. They fade with each wash. Natural dyes from plants are usually safe. Knowing dye types helps hair care.

Preventing and Minimizing Hair Damage
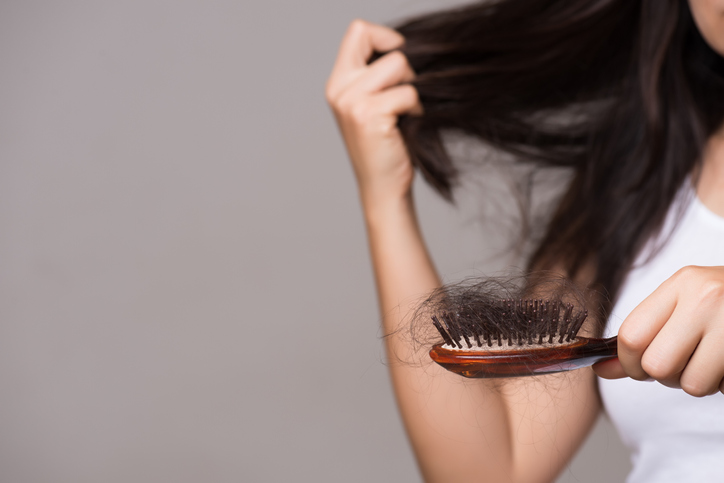
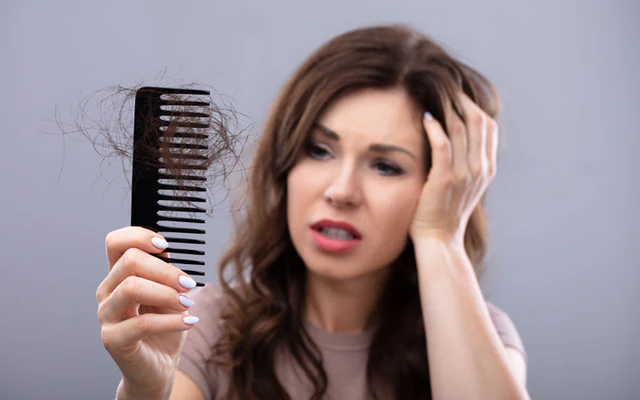
Hair coloring causes severe damage. It mostly affects the hair’s protein and cuticle structure. Thus, protein damage involves chemical dyes that break disulfide bonds. This makes hair more likely to break. Strong chemicals may reduce keratin, which causes dryness and loss of elasticity. Cuticle damage also involves a chemical process. It may be used to lift or roughen the cuticle layer. Porosity rises, leading to frizz and fading. Pre-color treatments, like deep conditioning and protein, strengthen hair. Post-color care includes sulfate-free shampoo, heat protectants, and regular conditioner. Reduce heat styling. Limit chemical treatments. Products like Olaplex repair bonds. These practices keep colored hair healthy.
Future Innovations in Hair Color
Hair dye gets better. New dyes match hair’s porosity. Gentle chemicals harm hairless. Bonding tech makes the color last. AI picks custom shades. VR shows color results. 3D printing makes custom hair. Genetic tests tailor color choices. AR apps let you try on colors. The future of yun nam hair care review dye is healthier and more personal.